

Learn how to secure your web applications from end to end. Explore both server-side and client-side security strategies to protect your systems and users. We focus on identifying vulnerabilities before attackers do, helping you maintain robust, resilient web applications. Whether you are a developer, business owner, or security enthusiast, our resources and tools make implementing web security straightforward. Join us to learn practical strategies and actionable techniques to make your applications safe and secure in today’s ever-evolving cyber landscape.
Secure your frontend with XSS prevention, CSP enforcement, and proper session management to protect user data and interactions.
Protect your servers, databases, and APIs from threats like SQL injection, CSRF, and improper authentication. Ensure your backend is secure and resilient.


Protect your backend systems with strong security mechanisms. We secure your servers, databases, and APIs from threats like SQL Injection, SSRF, authentication bypass, Access Control, and insecure storage. Our approach ensures your core infrastructure stays safe and resilient.

Authentication is the process of verifying that a user, device, or system is who or what it claims to be before granting access to resources like
Learn More
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) is a vulnerability where an attacker tricks a web server into making network requests that the attacker should not
Learn More
Business logic vulnerabilities are weaknesses in how an application’s rules, workflows, and decisions are designed, not just in its raw code.
Learn More
API testing is the process of sending requests directly to an API’s endpoints and checking that the responses meet expectations for functionality, reliability,
Learn More
Access control is a security practice that regulates who or what can view or use resources in a computing environment. It is a fundamental component of
Learn More
Path traversal (also called directory traversal) is a vulnerability where an application lets user input control a file path in an unsafe way,
Learn MoreClient-side security is all about protecting users right inside their browsers. When someone visits your website or uses your web app, they trust that everything they see — buttons, forms, scripts — is safe. Client-side security makes sure attackers can't tamper with what the user sees or interacts with.
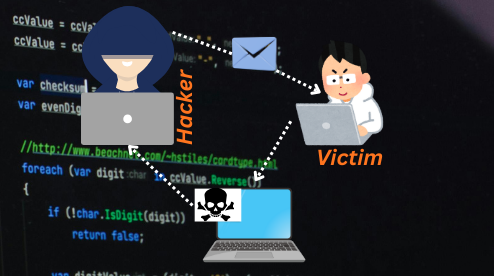
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a vulnerability where attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users,
Learn More
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a web vulnerability where a site is tricked into accepting an HTTP request that appears to come from an
Learn More
Clickjacking tricks users into clicking hidden elements on legitimate sites by overlaying invisible iframes. Attackers exploit this to perform
Learn More
The Document Object Model (DOM) represents HTML, XML, or SVG documents as a tree structure of objects in memory.
Learn More